Create a token collection
Many token creators generate non-fungible tokens in collections with a common theme or categorize their creative work by media, style, or subject. Creating a collection is similar to creating an individual non-fungible token as described in Create a non-fungible token except that:
- You need to create the collection to generate a unique identifier for it.
- You need to specify the collection a token is part of in its metadata file.
- You need to identify the collection to add a token to when you create the token.
You can use the built-in collection-policy to create the collection and identify the tokens that are part of the collection.
The collection-policy helps organize tokens into a curated group that can be uploaded and stored together.
The policy doesn't generate a collection of tokens.
If you use tools that automate token generation and metadata, you should evaluate the generated metadata to ensure that it conforms with the Marmalade metadata schema.
For demonstration purposes, the sample collection in this guide consists of portable network graphics.
Identify the collection
After you have created the artwork in a digital format, you can create the collection using the create-collection function in ChainWeaver.
To identify the collection:
-
Create a folder for the collection and move all of the digital artwork into the folder. In this example, the folder Luxi-Dupree contains the collection of digital images.
You can rename the files in the collection to use sequential numbering—for example, 1.jpg, 2.jpg, and so on—to make them easier to reference.
-
Open and unlock the Chainweaver desktop or web application.
-
Select Testnet as the network to connect to, click Contracts, then click Module Explorer.
-
Under Deployed Contracts, select the
marmalade-v2.collection-policycontract, then click View. -
Under Functions, select create-collection, then click Call.
-
On the Parameters tab, set the collection-name, collection-size, operator guard and operator-account information, then click Next.
-
Set the collection-name to the name you'll use in the token metadata. In this example, the collection name is
luxi-dupree. -
Set the collection-size to the number of tokens include in collection. In this example, the collection size is eight images.
-
Set the operator-guard to authorize a specific keyset or another guard to create the collection. In this example, the guard can be read from the transaction using
(read-keyset "my-keyset"). -
Set the operator-account to the account curating the token collection. In this example, the account is a single-key account with funds on the test network
k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e.
-
-
On the Configuration tab, select the Transaction Sender, review transaction settings, click Advanced to create or select the keyset to use, then click Next.
-
On the Sign tab, select an Unrestricted Signing key, then click Next.
-
On the Preview tab, scroll to see the Raw Response is true, then click Submit.
After you submit the transaction, it is queued for processing in the memory pool until validated and added to a block. After the transaction is included in a block, you can view the transaction results in the block explorer.

Successful collection creation You can find the collection identifier created for the collection in the transaction results. In this example, the collection identifier is "collection:MawFy7BSJMkatOJ07y_e0tYbPE26K_q8x0ACX5C25B8". You can use the collection identifier in the get-collection function to see the details for your collection. For example, you can use the get-collection function to see how many tokens have been added to the collection:
{ "id": "collection:MawFy7BSJMkatOJ07y_e0tYbPE26K_q8x0ACX5C25B8", "max-size": 8, "name": "luxi-dupree", "operator-account": "k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e", "operator-guard": KeySet { keys: [bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e], pred: keys-all }, "size": 0}{ "id": "collection:MawFy7BSJMkatOJ07y_e0tYbPE26K_q8x0ACX5C25B8", "max-size": 8, "name": "luxi-dupree", "operator-account": "k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e", "operator-guard": KeySet { keys: [bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e], pred: keys-all }, "size": 0}Because no tokens have been added to the collection yet, the
sizeis zero.
Upload the digital assets
As noted in Store digital assets, there are many ways you can store digital assets, including hosting the collection yourself, using a cloud service provider like Google or AWS, or uploading to a distributed file storage service like the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS).
There are also many tools available for uploading digital files for permanent storage. For example, you can use NFT.Storage with NFTUp, IPFS Desktop, Pinata, or any other tool to upload files and generate the content identifier (CID) for your work.
To upload the collection:
-
Upload the folder containing the collection to a storage location that provides permanent internet access to the digital asset.
In this example, uploading the
luxi-dupreefolder to IPFS generated the following content identifier and links:For the image file Uploaded example result Content identifier bafybeigzjyhvnq3ipdkipms2pd2ytebg3rb5mdqha5pytnitaeb7uel56yIPFS URL ipfs://bafybeigzjyhvnq3ipdkipms2pd2ytebg3rb5mdqha5pytnitaeb7uel56yGateway URL https://nftstorage.link/ipfs/bafybeigzjyhvnq3ipdkipms2pd2ytebg3rb5mdqha5pytnitaeb7uel56y -
Click the gateway URL to verify the assets in the collection are stored in IPFS.
-
Copy the IPFS URL for the collection to use in the metadata for each asset.
Create the metadata for each asset
Now that you have an content identifier that describes the location of each asset, you can create the metadata for each asset in the collection. In this example, the asset file names were left unchanged, but the metadata files use sequential numbering.
To create the metadata:
-
Create the metadata to describe each asset in the collection using the Marmalade metadata schema.
For example, the metadata for each asset—
1.json,2.json, and so on—might contain information similar to the following1.jsonmetadata file that describes thesleeping-on-dream-machine.jpgimage.{ "name": "Dupree and The Dream Machine", "description": "Dupree falls asleep on the couch with The Dream Machine as his pillow.", "image": "ipfs://bafybeigzjyhvnq3ipdkipms2pd2ytebg3rb5mdqha5pytnitaeb7uel56y/sleeping-on-dream-machine.jpg", "external_url": "https://bafybeigzjyhvnq3ipdkipms2pd2ytebg3rb5mdqha5pytnitaeb7uel56y.ipfs.nftstorage.link/sleeping-on-dream-machine.jpg", "authors": [ { "name": "Lola Pistola" } ], "collection": { "name": "luxi-dupree", "family": "Dogs" } }{ "name": "Dupree and The Dream Machine", "description": "Dupree falls asleep on the couch with The Dream Machine as his pillow.", "image": "ipfs://bafybeigzjyhvnq3ipdkipms2pd2ytebg3rb5mdqha5pytnitaeb7uel56y/sleeping-on-dream-machine.jpg", "external_url": "https://bafybeigzjyhvnq3ipdkipms2pd2ytebg3rb5mdqha5pytnitaeb7uel56y.ipfs.nftstorage.link/sleeping-on-dream-machine.jpg", "authors": [ { "name": "Lola Pistola" } ], "collection": { "name": "luxi-dupree", "family": "Dogs" } } -
Create a folder for the collection metadata. In this example, the folder luxi-dupree-metadata contains the metadata files for each asset in the collection of digital images.
-
Upload the folder containing the metadata files to IPFS.
In this example, uploading the luxi-dupree-metadata folder to IPFS generated the following content identifier and links:
For the JSON file Uploaded example result Content identifier bafybeic43pacmyel2bavpahsbrd4daknvizoyrpcsazxhrs6zmvwx5wlquIPFS URL ipfs://bafybeic43pacmyel2bavpahsbrd4daknvizoyrpcsazxhrs6zmvwx5wlquGateway URL https://nftstorage.link/ipfs/bafybeic43pacmyel2bavpahsbrd4daknvizoyrpcsazxhrs6zmvwx5wlqu -
Copy the content identifier for the metadata folder and append the name of each metadata file.
ipfs://bafybeic43pacmyel2bavpahsbrd4daknvizoyrpcsazxhrs6zmvwx5wlqu/1.jsonWith this step, you are ready to create and mint the non-fungible tokens in the collection.
Create a token identifier
Each token in the collection needs a unique identifier that links the token metadata to the collection identifier.
You can create token identifiers using the create-token-id function in the marmalade-v2.ledger contract.
As before, you can use the Chainweaver desktop or web application to navigate to contract functions and Testnet as the network to connect to
To create a token identifier:
-
In Chainweaver, click Contracts, then click Module Explorer.
-
Under Deployed Contracts, select the
marmalade-v2.ledgercontract, then click View. -
Under Functions, select create-token-id, then click Call.
-
On the Parameters tab, you need to specify the token-details and a creation-guard.
In this example, the token-details for the metadata file that describes the first token in the collection looks like this:
{ "uri": "ipfs://bafybeic43pacmyel2bavpahsbrd4daknvizoyrpcsazxhrs6zmvwx5wlqu/1.json", "precision": 0, "policies": [marmalade-v2.non-fungible-policy-v1,marmalade-v2.guard-policy-v1,marmalade-v2.collection-policy-v1]}{ "uri": "ipfs://bafybeic43pacmyel2bavpahsbrd4daknvizoyrpcsazxhrs6zmvwx5wlqu/1.json", "precision": 0, "policies": [marmalade-v2.non-fungible-policy-v1,marmalade-v2.guard-policy-v1,marmalade-v2.collection-policy-v1]}As this example illustrates, for the tokens in a collection, you should apply the built-in guard and collection policies. The guard policy protects the tokens from unauthorized activity and the collection policy is required to associate the tokens with the correct collection you've defined for them. To configure the guard policy, you'll need to register the accounts that can perform the activities you want to restrict access to. You'll register the guards for the guard policy when you create the token.
You can use (read-keyset "my-keyset") for the creation-guard to read the keyset from information you configure in the transaction details.
After configuring the parameters for the create-token-id function, click Next.
-
On the Configuration tab, select the Transaction Sender and, under Advanced, configure my-keyset by selecting a keyset predicate and a key, then click Next.
-
On the Sign tab, select an unrestricted signing key from the available Unrestricted Signing Keys, then click Next.
Note that you aren't required to select a transaction sender or a signing key to create a token identifier. However, this information is required to submit a transaction that records the token identifier in the blockchain.
-
On the Preview tab, scroll to see the Raw Response is a token identifier.
In this example, the token identifier created is "t:BRY_BIznnBWXuXlzKHg8Ha-s6k_4YTf1ctOfsz3CeWg".
You can click Submit to submit the transaction or copy the token identifier to use it when you create the token without sending the transaction to the blockchain. If you submit the transaction, you can view the results in the block explorer. If you choose to copy the identifier without submitting the transaction, close the create-token-id function call window.
Create a token
Now that you have prepared the collection and have a token identifier, you can create the token in the Marmalade ledger.
To create a token in a collection:
-
In Chainweaver, click Contracts, then click Module Explorer.
-
Under Deployed Contracts, select the
marmalade-v2.ledgercontract, then click View. -
Under Functions, select create-token, then click Call.
-
On the Parameters tab, you need to specify the token id, precision, uri, policies, and a creation-guard, then click Next.
In this example, the parameters look like this for the first token in the collection:
- id: "t:BRY_BIznnBWXuXlzKHg8Ha-s6k_4YTf1ctOfsz3CeWg"
- precision: 0
- uri: "ipfs://bafybeic43pacmyel2bavpahsbrd4daknvizoyrpcsazxhrs6zmvwx5wlqu/1.json"
- policies: [marmalade-v2.non-fungible-policy-v1,marmalade-v2.guard-policy-v1,marmalade-v2.collection-policy-v1]
- creation-guard: (read-keyset "my-keyset")
Be sure that the creation guard you specify here matches the operator guard you used to create the collection.
-
On the Configuration tab, review the transaction details, select the Transaction Sender, then click Advanced.
-
On the Keysets tab, type the keyset name, click Create, select a keyset predicate, and select a key.
Remember that you must use the same keyset that you used to create the collection.
-
Click the Raw tab to configure policy settings for the collection policy and the guard policy as a JSON object, then click Next.
In this example, the Raw data sets the collection identifier and registers the guards to use for the mint, burn, transfer, and sale operations. For example:
{ "collection_id": "collection:MawFy7BSJMkatOJ07y_e0tYbPE26K_q8x0ACX5C25B8", "mint-guard": { "keys": ["k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e"], "pred": "keys-all"}, "burn-guard": { "keys": ["k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e"], "pred": "keys-all"}, "sale-guard": { "keys": ["k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e"], "pred": "keys-all"}, "transfer-guard": { "keys": ["k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e"], "pred": "keys-all"}}{ "collection_id": "collection:MawFy7BSJMkatOJ07y_e0tYbPE26K_q8x0ACX5C25B8", "mint-guard": { "keys": ["k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e"], "pred": "keys-all"}, "burn-guard": { "keys": ["k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e"], "pred": "keys-all"}, "sale-guard": { "keys": ["k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e"], "pred": "keys-all"}, "transfer-guard": { "keys": ["k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e"], "pred": "keys-all"}}In this example, the same account is authorized to perform all token activity. You don't need to specify a guard for any token activity that you don't want to restrict access to. You can also use different guards for any token action if you want to authorize different accounts to perform specific actions.
-
On the Sign tab, select an unrestricted signing key from the available Unrestricted Signing Keys, then click Next.
-
On the Preview tab, review the transaction details, including the destination network and chain, and verify that the Raw Response is true, then click Submit.
After you submit the transaction, it is queued for processing in the memory pool until validated and added to a block. After the transaction is included in a block, you can view the transaction results in the block explorer.

Token added to the collection and the Marmalade ledger
Mint the collection token
Now that you have a token in the Marmalade ledger, you can mint the token using the account you registered for the mint guard.
To mint a non-fungible token in a collection:
-
Open and unlock the Chainweaver desktop or web application.
-
Select Testnet as the network to connect to the Kadena test network.
-
Click Contracts, then click Module Explorer.
-
Under Deployed Contracts, select the
marmalade-v2.ledgercontract, then click View. -
Under Functions, select mint, then click Call.
-
On the Parameters tab, set the id, account, guard, and amount information, then click Next.
In this example, the parameters look like this for the first token in the collection:
- id: "t:BRY_BIznnBWXuXlzKHg8Ha-s6k_4YTf1ctOfsz3CeWg"
- account: "k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e"
- guard: (read-keyset "my-keyset")
- amount: 1.0
Be sure to specify the account and guard you used to create the collection. The non-fungible policy ensures that only one token can be minted.
-
On the Configuration tab, select the Transaction Sender, review transaction settings, click Advanced to verify the keyset is the one you intend to use, then click Next.
-
On the Sign tab, click the Grant Capabilities plus (+) to add the MINT capability to the transaction and specify the token identifier, minting account, and amount as arguments.
In this example, the MINT capabilities look like this:
(marmalade-v2.ledger.MINT "t:BRY_BIznnBWXuXlzKHg8Ha-s6k_4YTf1ctOfsz3CeWg" "k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e" 1.0)(marmalade-v2.ledger.MINT "t:BRY_BIznnBWXuXlzKHg8Ha-s6k_4YTf1ctOfsz3CeWg" "k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e" 1.0) -
Select an account to sign for the coin.GAS and marmalade-v2.ledger.MINT capabilities, then click Next.
-
On the Preview tab, scroll to see the Raw Response is true, then click Submit.
After you submit the transaction, it is queued for processing in the memory pool until validated and added to a block. After the transaction is included in a block, you can view the transaction results in the block explorer.
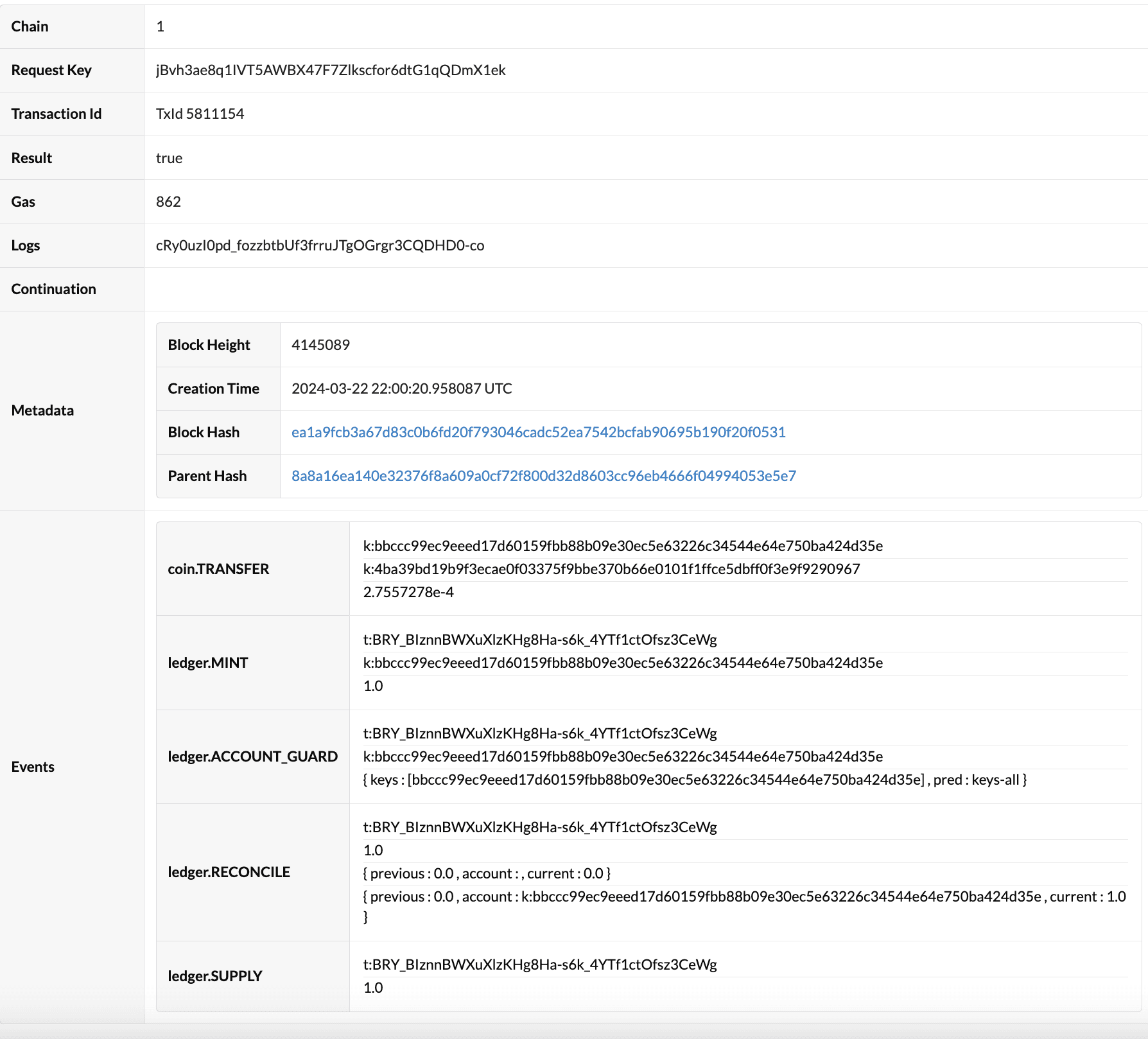
This example demonstrated the steps for creating and minting a single token in a collection.
You can call the get-collection function to verify that your token as been added to the collection.
For example, calling the get-collection function after completing the previous steps returns a collection size of 1:
{ "id": "collection:MawFy7BSJMkatOJ07y_e0tYbPE26K_q8x0ACX5C25B8", "max-size": 8, "name": "luxi-dupree", "operator-account": "k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e","operator-guard": KeySet { keys: [bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e], pred: keys-all }, "size": 1}{ "id": "collection:MawFy7BSJMkatOJ07y_e0tYbPE26K_q8x0ACX5C25B8", "max-size": 8, "name": "luxi-dupree", "operator-account": "k:bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e","operator-guard": KeySet { keys: [bbccc99ec9eeed17d60159fbb88b09e30ec5e63226c34544e64e750ba424d35e], pred: keys-all }, "size": 1}From here, you can create and mint the remaining tokens in your collection or offer the token for sale.
Start a sale with an offer
Now that your token is recorded in the Marmalade ledger, you can transfer it to another account or offer it for sale. In this simple example, there's no royalty policy associated with the token because it isn't intended to generate an ongoing revenue stream. However, the token owner can still offer the token for sale.
As you might remember from Token sales and trustless escrow, the offer is the first step in a sale pact. The offer can include a specific price that's not negotiable or be configured to use a specific type of sale contract with parameters to support a specific sales model. For example, you can configure a sale to use a conventional auction format or a dutch auction format to attract buyers to bid on the work. Each auction format is implemented as sales-specific smart contract that you can attach to a sale pact when you're ready to offer your tokens for sale.
You can find an introduction to sales-specific contracts—like the conventional and dutch auction contracts—in Layered contract architecture. For information about the difference between a conventional auction and a dutch auction, see Auctions
For technical details about the conventional auction contract, see Conventional auction sale contract. For technical details about the dutch auction contracts, see Dutch auction sale contract. For information about creating your own sales-specific contracts, see Create a sale contract.
Next steps
This guide demonstrated the workflow for creating a non-fungible token collection using the Marmalade standard with permanent storage on IPFS. To learn more about the policies configured in this example and other policies available, see Policies. To learn more about the selling tokens, see Sales.